A locale is a set of parameters which represents specific locale such as geographic region or political region that shares the same language and customs. A locale object may includes user’s language, country, and any special variant preferences that user needs. A Locale class which requires operation to perform its task is called as locale-sensitive and uses Locale to provide information for the user.
Locale object is a just an identifier for region, where Locale validity checking is not performed. For example, if we want to display the number which is referred as locale-sensitive operation where the number format should be formatted according to the customs and conventions of the user’s native country, region, or culture. A Locale is not a container for the objects, it is a just mechanism for identifying an objects.
also read:
Locale Class Declaration
public final class Locale
extends Object
implements Cloneable, Serializable
Locale Class Constructors
- Locale(String language(): This constructor creates new Locale from the specified language.
- Locale(String language, String country): This constructor specifies a Locale object with language and country code.
- Locale(String language, String country, String variant): This constructor creates a Locale object with language, country code and variant.
Locale Class Example
Below example demonstrate use of Locale class.
package locale;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Locale;
public class LocaleClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Locale locales[] = SimpleDateFormat.getAvailableLocales();
for (int i = 1; i <20; i++) {
System.out.printf("%10s - %s, %s \n" , locales[i].toString(),
locales[i].getDisplayName(), locales[i].getDisplayCountry());
}
}
}
- In the above example, we have used different methods i.e. getAvailableLocales(), getDisplayName() and getDisplayCountry( ) methods.
- The getAvailableLocales() method is used to get an array of object.
- The getDisplayName() method displays the name for current locale that user wants to display.
- The getDisplayCountry( ) method specifies the name for the locale’s country.
When you run the above example, you would get the following output: 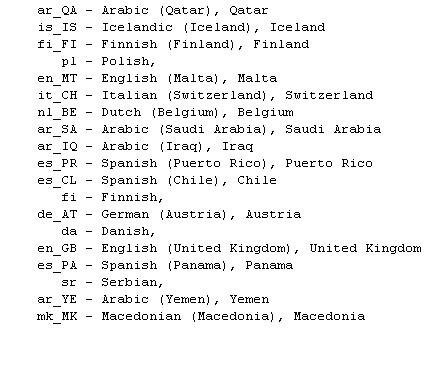
Locale Class Fields
| Fields | Description |
|---|---|
| static Locale CANADA | This field is constant for country en_CA. |
| static Locale CANADA_FRENCH | This field is constant for country fr_CA. |
| static Locale CHINA | This field is constant for country zh_CN. |
| static Locale CHINESE | This field is constant for language zh. |
| static Locale ENGLISH | This field is constant for language en. |
| static Locale FRANCE | This field is constant for country fr_FR. |
| static Locale FRENCH | This field is constant for language fr. |
| static Locale GERMAN | This field is constant for language de. |
| static Locale GERMANY | This field is constant for country de_DE. |
| static Locale ITALIAN | This field is constant for language it_CH. |
| static Locale ITALY | This field is constant for country it_IT. |
| static Locale JAPAN | This field is constant for country ja_JP. |
| static Locale JAPANESE | This field is constant for language ja. |
| static Locale KOREA | This field is constant for country ko_KR. |
| static Locale KOREAN | This field is constant for language ko. |
| static Locale PRC | This field is constant for country zh_CN. |
| static Locale ROOT | This field is constant for the root locale . |
| static Locale SIMPLIFIED CHINESE | This field is constant for language zh_CN . |
| static Locale TAIWAN | This field is constant for country zh_TW . |
| static Locale TRADITIONAL_CHINESE | This field is constant for language zh_TW . |
| static Locale UK | This field is constant for country en_GB . |
| static Locale US | This field is constant for country en_US . |
Locale Class Methods
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| Object clone() | This method returns copy of the cloneable object. |
| boolean equals(Object obj) | It compares this locale with another object and returns true if they are eqaul. |
| Locale [ ] getAvailableLocales() | This method returns the list of all system’s installed locales. |
| String getCountry() | It returns the country code for this locale. |
| Static Locale getDefault() | This method returns the user’s preferred locale. |
| String getDisplayCountry() | This method returns the name of the locale’s country, localized to locale. |
| String getDisplayLanguage() | This method returns a name for the locale’s language that the user wants to display. |
| String getDisplayLanguage(Locale) | This method returns a name for the locale’s language that user wants to display. |
| String getDisplayName() | This method returns a name for the locale that the user want to display. |
| String getDisplayName(Locale) | This method returns a name for the locale that the user want to display. |
| String getDisplayVariant() | This method returns variant name for the variant code in the default Locale. |
| String getDisplayVariant(Locale) | This method returns variant name for the variant code in the default Locale |
| String getISO3Country() | It returns three-letter ISO 3166 country code for this locale’s country. |
| String getISO3Language() | This method returns a three-letters ISO 639-2/T language code which is corresponds to the language code for this locale. |
| static String[ ] getISOCountries() | This method returns an array of all two-letter country code defined in ISO 3166. |
| static String[ ] getISOLanguages() | This method returns an array of all two-letter language codes defined in ISO 639. |
| String getLanguage() | This method returns the Locale language code which will be either empty string or lowercase. |
| String getVariant() | This method returns the locale variant code. |
| int hashCode() | This returns an integer hash code for this locale. |
| void setdefault(Locale) | This method is used to set default locale for this instance of the JVM(Java Virtual Machine). |
| String toString() | This method returns the string representation of this Locale which includes language country and variant. |
Locale Class Methods Example
package myproject;
import java.util.Locale;
class LocaleMethod {
public static void main(String[] a) {
Locale l = Locale.getDefault();
System.out.println(" Language, Country, Variant, Name");
System.out.println(" ");
System.out.println("Default locale: ");
System.out.println(" "+l.getLanguage()+", "+l.getCountry()+", "
+", "+l.getVariant()+", "+l.getDisplayName());
l = Locale.CANADA_FRENCH;
System.out.println("A predefined locale - Locale.CANADA_FRENCH:");
System.out.println(" "+l.getLanguage()+", "+l.getCountry()+", "
+", "+l.getVariant()+", "+l.getDisplayName());
l = new Locale("en", "CN");
System.out.println("User defined locale -Locale(\"en\",\"CN\"):");
System.out.println(" "+l.getLanguage()+", "+l.getCountry()+", "
+", "+l.getVariant()+", "+l.getDisplayName());
Locale[ ] s = Locale.getAvailableLocales();
System.out.println( "Supported locales: ");
for(int i = 1; i <=10; i++) {
System.out.println( " "+s[i].getLanguage()+", "
+s[i].getCountry( )+", "+s[i].getVariant()+", "
+s[i].getDisplayName( ));
}
}
}
- In the above example, we have used different methods such as getAvailableLocales(), getDisplayName(),getCountry( ), getVariant( ), getLanguage() methods.
- The getAvailableLocales() method is used to get an array of object.
- The getDisplayName() method displays the name for current locale that user wants to display.
- The getCountry( ) method specifies the country code for this locale.
- The getVariant( ) method specifies the variant code for this Locale.
- The getLanguage() method is used to get the language code for this Locale.
When you run the above example, you would get the following output: 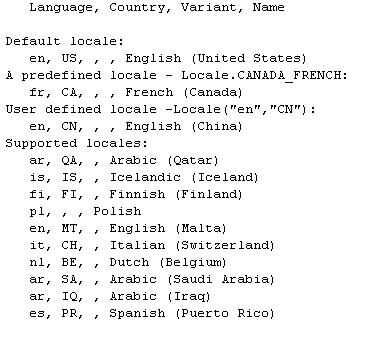

 Bootstrap Media Object
Bootstrap Media Object