The Math object provides a collection of properties of Number objects and methods. It is built in object which has properties and methods for mathematical constants and functions. It allows performing mathematical tasks. It has methods for trigonometric functions, such as sin( ), cos( ) and also used for mathematical operation.
Math is not constructor. All methods and properties of Math are static. These can be called by using Math as an object without creating it.
Javascript Math Object Syntax
var a= math.sqrt(4)
Properties
The following table shows properties of Math object:
| Properties | Description |
| E | It is a base of natural logarithm, Euler’s constant number is approximately 2.718. |
| LOG2E | It is Euler’s base 2 logarithm which is approximately 1.44 |
| LOG10E | It is Euler’s base 10 logarithm which is approximately 0.43 |
| PI | It is a constant value which cannot be altered, it’s approximate value is 3.141 |
| LN2 | It is used to specify the natural logarithm of 2. |
| LN10 | It is used to specify the natural logarithm of 10. |
| SQRT 1_ 2 | It is used to calculate the square root value of a1/2. |
| SQRT2 | It is used to calculate the square root value of a 2. |
Javascript Math Object Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="ISO-8859-1">
<title>Math object properties</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
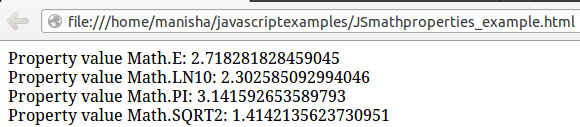
document.write("Property value is: " + Math.E);
document.write("<br>Property value is: " + Math.LN10);
document.write("<br>Property value is: " + Math.PI);
document.write("<br>Property value is: " + Math.SQRT2);
</script>
</body>
</html>
- <script type=”text/javascript”> tag is used to define client side script which uses attribute type for specifying MIME type.
- document.write(“Property value is: ” + Math.E); line displays Euler’s constant number which is approximately 2.718.
- document.write(“Property value is: ” + Math.LN10); line displays natural logarithm of 10.
- document.write(“Property value is: ” + Math.PI); line displays constant value which is approximate value is 3.141.
- document.write(“Property value is: ” + Math.SQRT2); line specifies square root value of a 2.
Example Application Test
- Save the file as JSmathproperties_example.html in your system.
- Just open the file in the browser, you will see the below picture in the browser.
When the execution process is completed successfully we will get the following output:
Methods
The following table shows methods of Math object:
| Methods | Description |
| cos( ) | It is used to specifies the cosine of the number. |
| sin( ) | It is used to specifies the sine of the number. |
| tan( ) | It is used to specifies the tangent of the number. |
| max( ) | It is used to represent the largest number. |
| min( ) | It is used to represent the minimum number. |
| log( ) | It is used for natural logarithm (base E). |
| exp( ) | It is used for exponential power of logarithm i.e. e^x |
| pow( ) | It is used for base to the exponent i.e. base^exponent |
| sqrt( ) | It is used to calculate the square root value of a given number. |
| floor( ) | It is used to get the biggest integer which is less then or equal to a number. |
| random( ) | It is used to generate a random number from 0 to 1. |
| round( ) | It is used to round up the figure to its nearest number. |
| abs( ) | It is used to get the absolute value of the number. |
| acos( ) | It is used to specifies the arccosine of the number. |
| asin( ) | It is used to specifies the arcsine of the number. |
| atan( ) | It is used to specifies the arctangent of the number. |
| atan2( ) | It is used to specifies the arctangent of the quotient of its argument. |
| ceil ( ) | It is used to get the smallest integer which is greater than or equal to a number |
Javascript Math Object Methods Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="ISO-8859-1">
<title>Math object methods</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
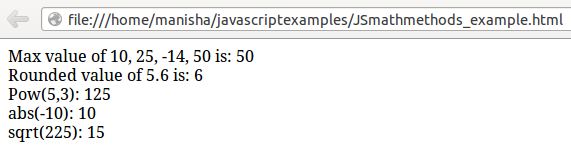
document.write("Max value of 10, 25, -14, 50 is: " + Math.max(10, 25, -14, 50));
document.write("<br>Rounded value of 5.6 is: " + Math.round(5.6));
document.write("<br>Pow(5,3): " + Math.pow(5, 3));
document.write("<br>abs(-10): " + Math.abs(-10));
document.write("<br>sqrt(225): " + Math.sqrt(225));
</script>
</body>
</html>
- <script type=”text/javascript”> tag is used to define client side script which uses attribute type for specifying MIME type.
- document.write(“Property value is: ” + Math.max(10, 25, -14, 50)); line specifies largest number in the given arguments.
- document.write(“Property value is: ” + Math.round(5.6)); line round up the figure to its nearest number .
- document.write(“Property value is: ” + Math.pow(5, 3)); line returns base to the exponent power.
- document.write(“Property value is: ” + Math.abs(-10)); line returns absolute value of a number.
- document.write(“Property value is: ” + Math.sqrt(225)); line returns square root of a number.
Example Application Test
- Save the file as JSmathmethods_example.html in your system.
- Just open the file in the browser, you will see the below picture in the browser.
Output
When the execution process is completed successfully we will get the following output:

 JSF 2 SystemEventListener – UIViewRoot Events Example
JSF 2 SystemEventListener – UIViewRoot Events Example