Ajax mechanism is identical to those mechanisms that considered as error-prone, as you have experienced when you’re working with a JSF framework. Ajax framework with the JSF 2.0 framework provides you onerror attribute to handle the errors that could be thrown while the JSF framework executes the component(s) that mentioned at f:ajax’s execute attribute
Also Read:
The value of the onerror attribute is a JavaScript function. JSF calls that function when there’s an error during the processing of the Ajax request. Like f:ajax’s onevent attribute, JSF passes the onerror function data object. The values for that object are the same as the values for the data object that JSF passes to the event function, as listed:
- httpError: Response status null or undefined or status < 200 or status >=300.
- emptyResponse: There was no response from the server.
- maleformed: The response was not well-formed XML.
- serverError: The Ajax response contains an error element from the server.
For errors, the data object also contains three properties not present for events:
- description
- errorName
- errorMessage
1. The View
index.xhtml
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:ui="http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets"
xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html"
xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core">
<h:head>
<script>
if(!net) var net = {}
if(!net.javabeat){
net.javabeat = {
monitor:
function (data){
var loading = document.getElementById("image");
if(data.status == "begin"){
loading.style.display = "block";
}
else if(data.status == "success"){
loading.style.display = "none";
}
},
handle:
function(data){
console.log("Error Description: "+data.description);
console.log("Error Name: "+data.errorName);
console.log("Error errorMessage: "+data.errorMessage);
console.log("httpError: "+data.httpError);
console.log("emptyResponse: "+data.emptyResponse);
console.log("maleformed: "+data.maleformed);
console.log("serverError: "+data.serverError);
}
}
}
</script>
<h:outputScript library="javax.faces" name="jsf.js"/>
</h:head>
<h:body>
<f:view>
<h1>JavaBeat JSF 2.2 Examples</h1>
<h2>JSF2 Using JavaScript Namespace Example</h2>
<h:form prependId="false">
<h:inputText id="input" value="#{indexBean.message}"/>
#{' '}
<h:commandButton value="Display Text" action="#{indexBean.action}">
<f:ajax execute="@this input" render="output"
onevent="net.javabeat.monitor" onerror="net.javabeat.handle"></f:ajax>
</h:commandButton>
#{' '}
<h:outputText id="output" value="#{indexBean.message}"></h:outputText>
<h:graphicImage id="image" value="#{resource['images:ajax-loader.gif']}" style="display:none;"></h:graphicImage>
</h:form>
</f:view>
</h:body>
</html>
2. Managed Bean
IndexBean.java
package net.javabeat.jsf;
import javax.faces.bean.ManagedBean;
import javax.faces.bean.SessionScoped;
@ManagedBean
@SessionScoped
public class IndexBean {
private String message;
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public String action() throws Exception{
Thread.sleep(6000);
System.out.println(5+10/0); // This is an assumption
System.out.println(message);
return "";
}
}
3. The Deployment Descriptor (web.xml)
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="2.5" metadata-complete="true"> <context-param> <description>State saving method: 'client' or 'server' (=default). See JSF Specification 2.5.2 </description> <param-name>javax.faces.STATE_SAVING_METHOD</param-name> <param-value>client</param-value> </context-param> <context-param> <param-name>javax.faces.application.CONFIG_FILES</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/faces-config.xml</param-value> </context-param> <servlet> <servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>javax.faces.webapp.FacesServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/faces/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.xhtml</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <listener> <listener-class>com.sun.faces.config.ConfigureListener</listener-class> </listener> </web-app>
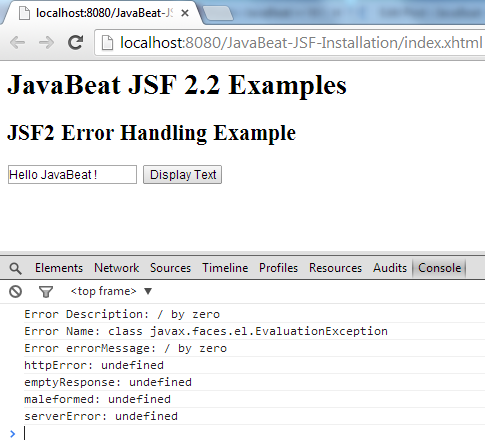
4. JSF 2 Handling Ajax Error Demo
The below snapshot shows you how could you handle the errors that might be occurred while the Ajax request being processed.
[wpdm_file id=33]

 JSF 2 Ajax Progress Bar Example
JSF 2 Ajax Progress Bar Example