When you implement a web application, it’s good idea to collect message strings in a central location. This process makes it easier to keep messages consistent and, crucially, makes it easier to localize your application for other locales.
The messages strings are collected in a file(s) in the properties format, and those files must use the extension .properties. you can declare the message bundle in two ways. The simplest way is to supply file named faces-config.xml in the WEB-INF directory of your application. Instead of using a global resource bundle declaration, you can add f:loadBundle element to each JSF page that needs access to the bundle. In either case, the messages in the bundle are accessible through a map variable that defined in the both way.
Also Read:
When you localize a bundle file, you need to add a locale suffix to the file name: an underscore followed by the lowercase, two-letter ISO-639 language code (you can find a listing of all two- and three-letter ISO-639 language codes at this link).
1. Managed Bean
IndexBean.java
package net.javabeat.jsf;
import java.util.Locale;
import javax.faces.bean.ManagedBean;
import javax.faces.bean.SessionScoped;
import javax.faces.context.FacesContext;
@ManagedBean
@SessionScoped
public class IndexBean {
private String locale = "en";
public String getLocale() {
return locale;
}
public void setLocale(String locale) {
this.locale = locale;
}
public String changeLocale(String locale){
// Change the locale attribute
this.locale = locale;
// Change the locale of the view
FacesContext.getCurrentInstance().getViewRoot().setLocale(new Locale(this.locale));
return "";
}
}
2. faces-cofig.xml
faces-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <faces-config xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-facesconfig_2_2.xsd" version="2.2"> <application> <resource-bundle> <base-name>net.javabeat.jsf.application</base-name> <var>msg</var> </resource-bundle> </application> </faces-config>
3. The View
index.xhtml
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:ui="http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets"
xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html"
xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core"
xmlns:c="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core">
<h:head>
<title><h:outputText value="#{msg.title}"/></title>
</h:head>
<h:body>
<h:form id="form">
<f:loadBundle var="messages" basename="net.javabeat.jsf.messages"></f:loadBundle>
<h1>
<h:outputText value="#{msg.head}" />
</h1>
<h2>
<h:outputText value="#{msg.example_name}" />
</h2>
<h:outputText value="#{msg.hello_message}"/>
<br/>
<br/>
<h:outputText value="#{messages.inlineLoad}"/>
<br/>
<br/>
<h:commandButton value="#{messages.german}" action="#{indexBean.changeLocale('de')}" rendered="#{indexBean.locale == 'en'}"/>
<h:commandButton value="#{messages.english}" action="#{indexBean.changeLocale('en')}" rendered="#{indexBean.locale == 'de'}"/>
</h:form>
</h:body>
</html>
4. The Properties Files
The below snapshot shows you the bundle properties files that already located at the classpath.
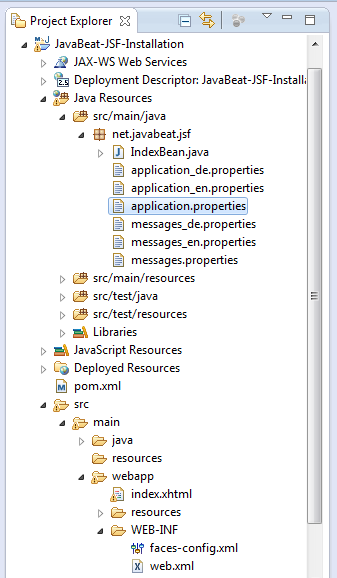
- Review the attached zip file for viewing the messages files.
5. The Deployment Descriptor (web.xml)
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="2.5" metadata-complete="true"> <context-param> <description>State saving method: 'client' or 'server' (=default). See JSF Specification 2.5.2</description> <param-name>javax.faces.STATE_SAVING_METHOD</param-name> <param-value>client</param-value> </context-param> <context-param> <param-name>javax.faces.application.CONFIG_FILES</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/faces-config.xml</param-value> </context-param> <servlet> <servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>javax.faces.webapp.FacesServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/faces/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.xhtml</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <listener> <listener-class>com.sun.faces.config.ConfigureListener</listener-class> </listener> </web-app>
6. JSF 2 Message Bundle Demo
The below snapshots will show you the complete scenario of using the message bundle properties for achieving a localization. The languages that are selected for such that demonstration are English and German.
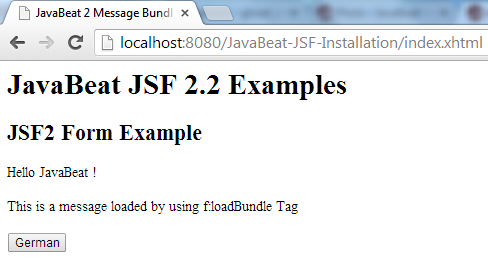
- The default locale for the application is an English, cause the browser is defaulted as English.
- Once the user has clicked on the German action, the form will be submitted and the action change locale will be executed.
- Once the action have been executed the FacesContext should change the locale using getViewRoot().setLocale.
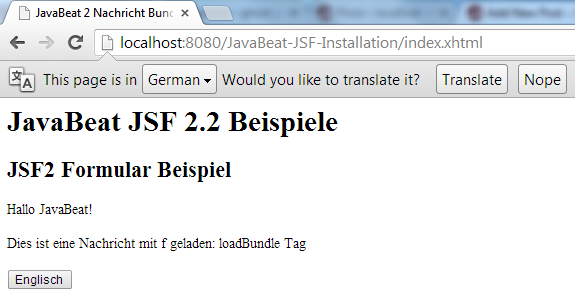
- The Locale have been changed.
- The german properties have been loaded and used.
- The ability to return back into English locale is already been exist by clicking on the English action that displayed using the german locale.

 JSF 2 Form Example
JSF 2 Form Example