The System Events are normally specified in the JavaServer Faces Specification 2.2 under “System Events” Subject. This concept expands on the idea of lifecycle PhaseEvents. With the PhaseEvents, it is possible to have an application scoped PhaseListeners that are given the opportunity to act on the system before and after each phase in the lifecycle. System events provide a much more fine-grained insight into the system, allowing application or component scoped listeners to be notified of a verity of kinds of events.
There are several ways to declare interest in a particular kind of event.
- Call Application.subscribeToEvent () to add an application scoped listener.
- Call UIComponent.subscribeToEvent () to add a component scoped listener.
- Use <f:event> tag to declare a component scoped listener.
- Use @ListenerFor or @ListenersFor annotation. The scope of the listener is determined by the code that processes the annotation. (This mechanism can be useful for component developers).
- Use <system-event-listener> element in an application configuration resource to add an application scoped listener.
At this tutorial, you are going to examine the using of <system-event-listener> in an application configuration to add application scoped listener.
Also Read:
1. Managed Bean
IndexBean.java
package net.javabeat.jsf;
import javax.faces.bean.ManagedBean;
import javax.faces.bean.SessionScoped;
@ManagedBean
@SessionScoped
public class IndexBean {
private String message;
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}
2. The View
index.xhtml
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:ui="http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets" xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core"> <f:view> <h:form> <h1>JavaBeat JSF 2.2 Examples</h1> <h2>JSF2 System Events - Application Source Example</h2> <br/> <h2>This is a JSF View</h2> </h:form> </f:view> </html>
3. SystemEventListener
SystemEventsListener.java
package net.javabeat.jsf.listener;
import javax.faces.application.Application;
import javax.faces.event.AbortProcessingException;
import javax.faces.event.SystemEvent;
import javax.faces.event.SystemEventListener;
public class SystemEventsListener implements SystemEventListener{
@Override
public void processEvent(SystemEvent event) throws AbortProcessingException {
// The handling of event
System.out.println("System Event Being Processed :: "+event.toString());
}
@Override
public boolean isListenerForSource(Object source) {
if(source instanceof Application){
// This listener for this kind of source
return true;
}
// This listener isn't for this kind of source
return false;
}
}
4. Faces Configuration File
faces-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <faces-config xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-facesconfig_2_2.xsd" version="2.2"> <application> <resource-bundle> <base-name>net.javabeat.jsf.application</base-name> <var>msg</var> </resource-bundle> <system-event-listener> <system-event-listener-class>net.javabeat.jsf.listener.SystemEventsListener</system-event-listener-class> <system-event-class>javax.faces.event.PostConstructApplicationEvent</system-event-class> </system-event-listener> <system-event-listener> <system-event-listener-class>net.javabeat.jsf.listener.SystemEventsListener</system-event-listener-class> <system-event-class>javax.faces.event.PreDestroyApplicationEvent</system-event-class> </system-event-listener> </application> </faces-config>
5. JSF 2 SystemEventListener Demo
The below snapshots show you the way that used for listening the SystemEventListener.
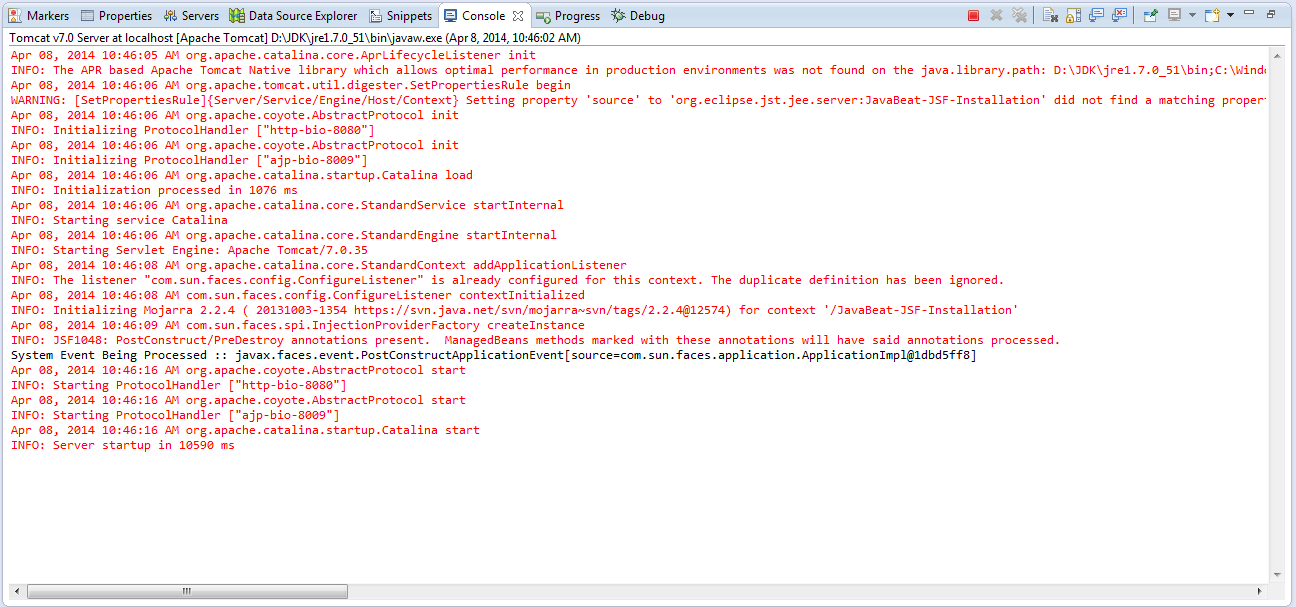
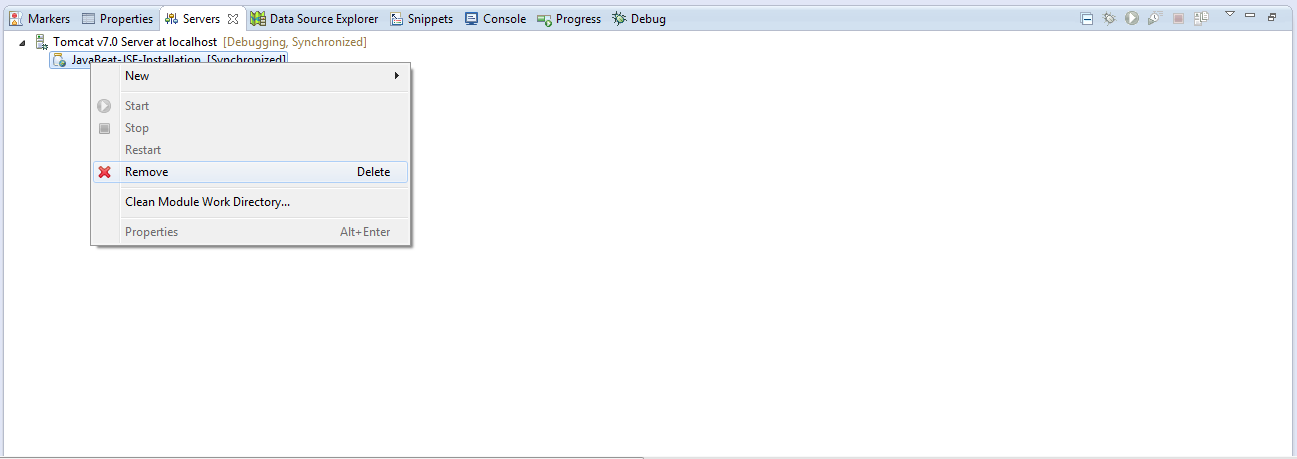
- By removing the application from the server, you are fired the PreDestroyApplicationEvent.
![]()
[wpdm_file id=52]

 JSF 2 DataTable Delete Row Example
JSF 2 DataTable Delete Row Example