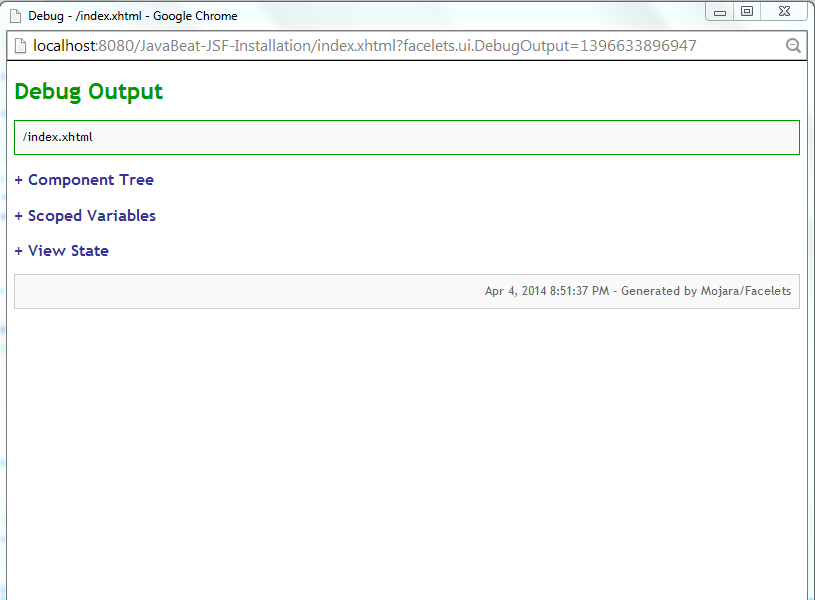
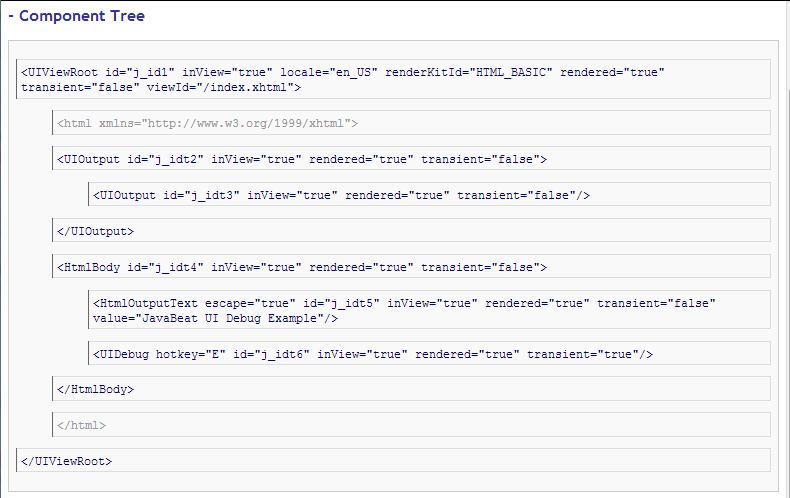
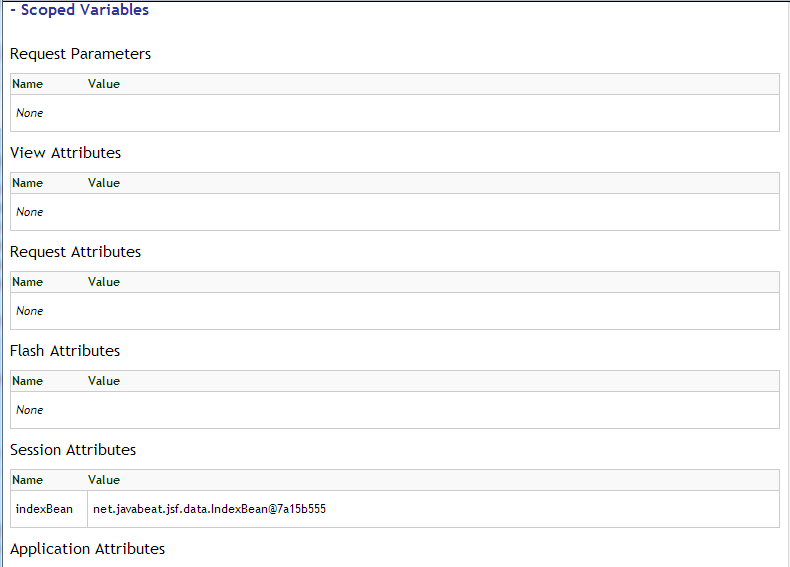
When you place the ui:debug tag in a Facelets page, a debug component is added to the component tree for that tag. If the user types a hotkey, which by default is CTRL+SHIFT+d, JSF opens a window and display the state of the component tree and the application’s scoped variables.
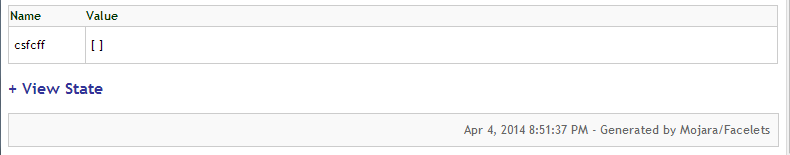
You can click on the Component Tree or Scoped Variables, to show the component tree or the application’s scoped variables, respectively. The ui:debug tag also lets you redefine the hotkey that bring up the Debug Output window, with a hotkey attribute.
The ui:debug component is very useful during the development, so developers can instantly see the current page’s component tree and the application’s scoped variables; however, you will probably want to remove the tag in production. For that reason, we recommend that you put the ui:debug tag in a template, where is is specified in one place, and shared among many views, instead of replacing the tag in each view’s XHTML page.
Also Read:
1. Managed Bean
IndexBean.java
package net.javabeat.jsf.data;
import javax.faces.bean.ManagedBean;
import javax.faces.bean.SessionScoped;
@ManagedBean
@SessionScoped
public class IndexBean {
private String message = "JavaBeat UI Debug Example";
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}
2. The Template
JavaBeatTemplate.xhtml
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:ui="http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets"
xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html"
xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core">
<h:head>
<h:outputScript library="javax.faces" name="jsf.js"/>
</h:head>
<h:body>
<ui:insert name="body"/>
<!-- The letter e is used, cause the CTRL+SHIFT+d is reserved for chrome browser -->
<ui:debug hotkey="e"/>
</h:body>
</html>
3. The View
index.xhtml
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:ui="http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets"
xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html"
xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core">
<h:head>
<h:outputScript library="javax.faces" name="jsf.js"/>
</h:head>
<h:body>
<ui:composition template="/template/JavaBeatTemplate.xhtml">
<ui:define name="body">
<h:outputText value="#{indexBean.message}"/>
</ui:define>
</ui:composition>
</h:body>
</html>
4. JSF 2 UI Debug Demo
The below snapshot shows you how could you debugging your view through using of ui:debug.
[wpdm_file id=45]

 JSF 2 UI Remove Example
JSF 2 UI Remove Example