When you run an application in the development project stage and you encounter an error, you get an error message in an undesirable form. You probably don’t want your users to see that message in such that ugly way.
To substitute a better error page, use error-page tag in the web.xml file, in that you can specify either a Java Exception or an HTTP error code. So in case the type of thrown exception has matched that type mentioned in the web.xml exception-type or the error code that generated by the server has matched error-code that mentioned in the web.xml, the JSF framework will handle it by forwarding the user into the desired view that you’ve defined for such those errors or exceptions.
1. The Deployment Descriptor
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="2.5" metadata-complete="true"> <error-page> <error-code>404</error-code> <location>/faces/error.xhtml</location> </error-page> <error-page> <error-code>500</error-code> <location>/faces/error.xhtml</location> </error-page> <error-page> <exception-type>java.lang.Exception</exception-type> <location>/faces/error.xhtml</location> </error-page> <context-param> <description>State saving method: 'client' or 'server' (=default). See JSF Specification 2.5.2 </description> <param-name>javax.faces.STATE_SAVING_METHOD</param-name> <param-value>server</param-value> </context-param> <context-param> <param-name>javax.faces.application.CONFIG_FILES</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/faces-config.xml</param-value> </context-param> <servlet> <servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>javax.faces.webapp.FacesServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/faces/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.xhtml</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <listener> <listener-class>com.sun.faces.config.ConfigureListener</listener-class> </listener> </web-app>
- The error codes that being handled in that defined web.xml are 500 and 400.
- The exceptions that being handled in that defined web.xml is the root of exceptions that could be thrown java.lang.Exception.
- All of the defined error codes and exceptions must be handled in a compelling error page called error.xhtml.
2. Faces Configuration File
faces-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <faces-config xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-facesconfig_2_2.xsd" version="2.2"> <application> <resource-bundle> <base-name>net.javabeat.jsf.application</base-name> <var>msg</var> </resource-bundle> </application> </faces-config>
- No changes are made on the faces configuration to support the error page concept
3. The Error Page
error.xhtml
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:ui="http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets"
xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html"
xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core">
<h1>JavaBeat JSF 2.2 Examples</h1>
<h2>JSF2 - Error Handling</h2>
<br />
<h:outputText value="Error Code: #{errorHandler.statusCode}"></h:outputText>
<br />
<h:outputText value="Error Desscription: #{errorHandler.message}"></h:outputText>
<br />
<h:outputText value="Exception Type: #{errorHandler.exceptionType}"></h:outputText>
<br />
<h:outputText value="Exception Calss: #{errorHandler.exception}"></h:outputText>
<br />
<h:outputText value="Request URI : #{errorHandler.requestURI}"></h:outputText>
</html>
4. ErrorHandler RequestScoped Bean
ErrorHandler.java
package net.javabeat.jsf.error;
import javax.faces.bean.ManagedBean;
import javax.faces.bean.RequestScoped;
import javax.faces.context.FacesContext;
@ManagedBean
@RequestScoped
public class ErrorHandler {
public String getStatusCode(){
String val = String.valueOf((Integer)FacesContext.getCurrentInstance().getExternalContext().
getRequestMap().get("javax.servlet.error.status_code"));
return val;
}
public String getMessage(){
String val = (String)FacesContext.getCurrentInstance().getExternalContext().
getRequestMap().get("javax.servlet.error.message");
return val;
}
public String getExceptionType(){
String val = FacesContext.getCurrentInstance().getExternalContext().
getRequestMap().get("javax.servlet.error.exception_type").toString();
return val;
}
public String getException(){
String val = (String)((Exception)FacesContext.getCurrentInstance().getExternalContext().
getRequestMap().get("javax.servlet.error.exception")).toString();
return val;
}
public String getRequestURI(){
return (String)FacesContext.getCurrentInstance().getExternalContext().
getRequestMap().get("javax.servlet.error.request_uri");
}
public String getServletName(){
return (String)FacesContext.getCurrentInstance().getExternalContext().
getRequestMap().get("javax.servlet.error.servlet_name");
}
}
- The error handler bean is defined as RequestScoped
- Several objects related to the error are placed in the Request Map and they are considered as Servlet Exception Attributes
5. Error Prone Page
index.xhtml
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:ui="http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets"
xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html"
xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core">
<f:view>
<h:form prependId="false">
<h1>JavaBeat JSF 2.2 Examples</h1>
<h2>JSF2 - Error Handling</h2>
<br/>
<h:outputText value="#{indexBean.message}"></h:outputText>
<h:commandButton value="Throws Exception" action="#{indexBean.navigate}"/>
</h:form>
</f:view>
</html>
6. Error Prone Managed Bean
IndexBean.java
package net.javabeat.jsf;
import javax.faces.bean.ManagedBean;
import javax.faces.bean.SessionScoped;
@ManagedBean
@SessionScoped
public class IndexBean {
private String message;
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public String navigate(){
// Assume an exception has been thrown by some business logic
System.out.println(10/0);
return "anonymousView";
}
}
7. JSF Error Handling Demo
The below snapshots show you how could a thrown exception being handled in a compelling view.
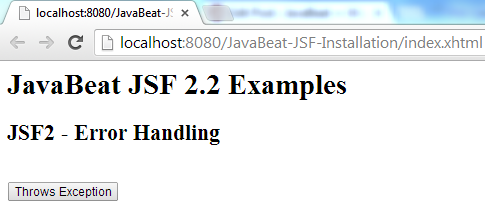
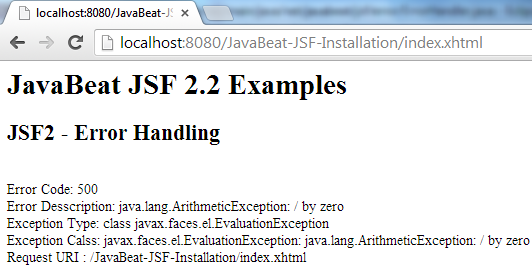
8. JSF Without Custom Error Page
The below snapshot shows you the ugly page that might be displayed for the users while they are navigating your site.
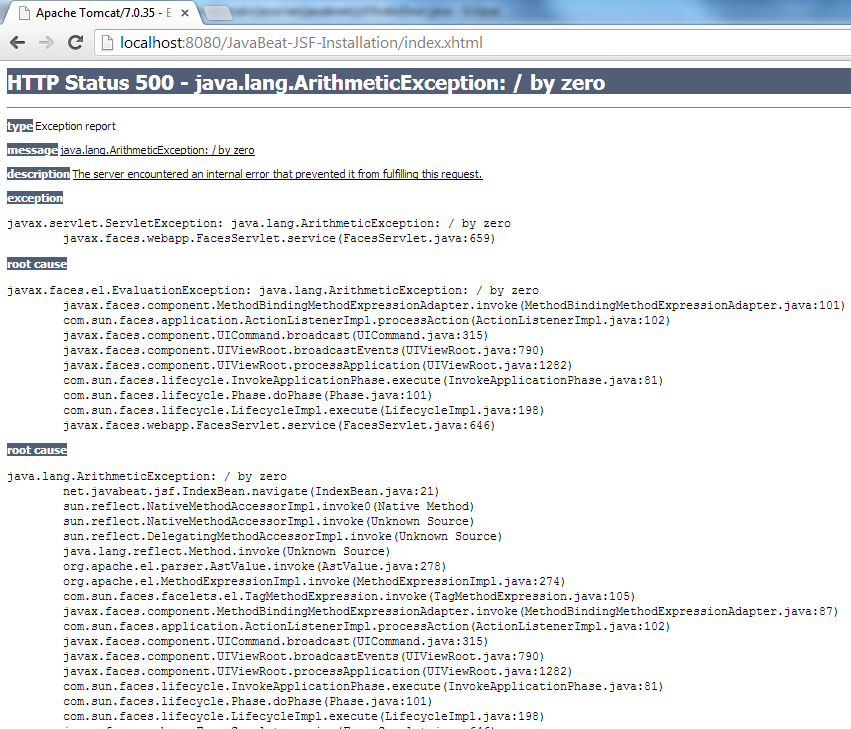
[wpdm_file id=57]

 Eclipse Tips : Type Filters in Eclipse
Eclipse Tips : Type Filters in Eclipse