In Java, a “for” loop is vital to iterate along the values in an increasing or decreasing manner. This iteration can be applied in a custom manner in the case of retrieving some specific values i.e., even or odd based on the requirements. This iteration assists in streamlining the code by minimizing it and utilizing a single functionality i.e., loop multiple times differently.
This article will demonstrate how to increment a “for” loop by “2” in Java.
How to Increment a Java for Loop by 2?
A “for” loop is applied to perform the iteration upon the given values in a range. These values can comprise multiple data types and can be placed in a container i.e., array, etc. Usually, this loop is used to iterate along each of the values individually. However, it can also be applied to perform the iteration in a custom manner.
Example 1: Incrementing a “for” Loop by 2 in Java
This example increments a “for” loop with a step of “2”:
public class For2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i+=2) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}}
In the above code lines:
- Specify a “for” loop that iterates along the values from “0” till “7” with a step of “2” using the “addition assignment operator (+=)”.
- It is such that upon each iteration, the iterated values will be incremented by “2”.
- Lastly, return the iterated values.
Output

Here, it can be verified that the specified values are iterated by “2” accordingly, thereby returning the even integers only.
Example 2: Decrementing a “for” Loop by 2 in Java
In this specific demonstration, a “for” loop can be decremented instead by “2”:
public class For2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
for (int i = 8; i > 0; i-=2) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}}
According to this block of code:
- Include a “for” loop that decrements the values starting from “8” till “1” via the “subtraction assignment operator (-=)”.
- After that, display the reversely iterated values.
Output
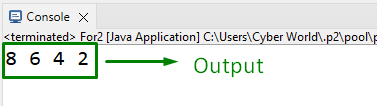
This outcome implies that the values specified in the “loop” are iterated appropriately.
Conclusion
By default, a “for” loop in Java increments by “1” but it can be incremented or decremented by “2” with the help of the addition assignment operator “+=”. This increment or decrement can be achieved in a custom manner with any values as per the requirement. This article demonstrated to increment a Java “for” loop by “2”.
